Finding the right light for your home used to be simple—you chose between basic bulbs like incandescents, CFLs, or halogens. But now, the lighting aisle at the hardware store can seem like a dizzying sea of confusing options.
But what do we actually know about the potential impacts, both positive and negative, of different lighting technologies? As consumers become more concerned about the effects of lighting on health and the environment, there’s a growing temptation to stick to the bulbs we know best.
However, new research suggests even familiar bulbs like CFLs could have hidden harms. So which bulbs provide the best balance of safety, health support, and sustainability? This article will decode the terminology around modern bulbs and delve into the latest science on how lighting affects the eyes, sleep, and circadian rhythms.
You’ll learn the key factors to evaluate when choosing bulbs for your unique needs. We’ll demystify up-and-coming lighting technologies like _______ (keep it a mystery!), explaining their possible benefits as well as areas of concern. Let’s shine a light on the health and environmental impacts of today’s lighting options to help you make the most informed, responsible choice for your home.
History of the Lightbulb
It began in the early 19th century, which introduced the concept of electric light through arc lamps. Practical incandescent bulbs truly took shape in the late 19th century with Thomas Edison’s invention of the bamboo filament incandescent bulb, which lasted over 1,200 hours. These bulbs operated by passing an electric current through a filament, usually made of tungsten, causing it to emit visible light.
As the 20th century dawned, fluorescent lighting technology emerged. Fluorescent bulbs function by passing a current through a mixture of argon and mercury vapor, creating ultraviolet light that interacts with a phosphorescent coating, ultimately producing visible light. This technology paved the way for compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) in the later part of the century.
The late 20th century also witnessed the birth of Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). LEDs operate on electroluminescence, where a semiconductor emits light when an electric current flows through it.
In terms of environmental impact, incandescent bulbs contain no hazardous materials, while CFLs contain mercury, necessitating careful disposal. LEDs, on the other hand, can contain carcinogens like lead or arsenic may be present in many electronic components.
Dangers Of LED Lights
As LED lights continue to revolutionize modern lighting solutions, it’s important to recognize not only their advantages but also the potential environmental and health concerns associated with their use. One significant concern centers around the release of toxic substances, notably mercury, when LED bulbs are broken.
A comprehensive study conducted by researchers from Germany’s Federal Environmental Agency shed light on this issue, revealing that in the event of an indoor breakage, energy-efficient lightbulbs can discharge mercury into the air at concentrations that are a staggering 20 times higher than what is considered safe for human exposure.
This poses a serious health risk, as mercury is a potent neurotoxin that can have detrimental effects on the nervous system, potentially leading to symptoms ranging from headaches and migraines to fatigue, seizures, anxiety, insomnia, and difficulties in concentration.
In addition to mercury, further research published in late 2010 in the journal Environmental Science and Technology has uncovered that LEDs may harbor a range of other potentially hazardous substances, including lead and arsenic. The presence of these materials raises concerns regarding their safe disposal and potential environmental impact.
A particularly noteworthy concern is the potential impact of LED lights on eye health. Researchers in Spain have made significant strides in understanding the effects of blue LED light on the human retina. Their findings indicate that prolonged or excessive exposure to blue LED light can lead to cellular damage in the retina, potentially resulting in vision impairment or even blindness over an extended period.
Furthermore, modern light bulbs, including energy-efficient variants, have been found to contain carcinogenic substances. A study conducted by Germany’s Alab Laboratory has identified a number of these carcinogens, including phenol, naphthalene, and styrene.
These substances are commonly used in chemical manufacturing processes, and their presence in light bulbs raises concerns about potential health risks associated with long-term exposure.
Additionally, it is crucial to address the issue of light pollution stemming from LED lightbulbs. The high-intensity and directional nature of LED lighting can contribute significantly to the phenomenon of light pollution.
This not only disrupts natural ecosystems and wildlife behavior but also impacts human health and wellbeing, disrupting sleep patterns and contributing to various health issues.
Dangers Of Handling Broken LED Bulbs
Given the potential risks associated with LED bulbs, the U.S. government has issued specific guidelines for handling bulb breakages. In the event of breakage, it is recommended to not only carefully clean the area but also to open all windows and doors for ventilation, and to vacate the space for at least 15 minutes.
Moreover, due to the hazardous materials they contain, LED bulbs should never be disposed of in regular household waste. Instead, it is crucial to take them to designated toxic waste facilities for proper disposal, in order to minimize their environmental impact.
In conclusion, while LED lights offer significant advantages in terms of energy efficiency and lifespan, it is vital to be cognizant of the potential risks associated with their use, particularly in the event of breakage. Proper handling and disposal methods are essential to mitigate potential health and environmental hazards, including the impact of light pollution on our ecosystems and well-being.
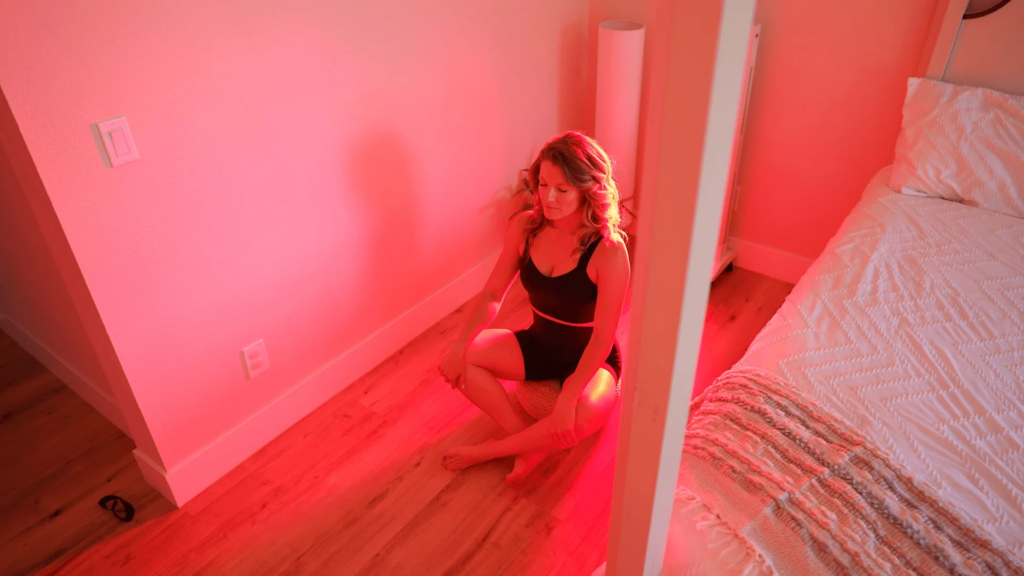
Red And Near-Infrared Light Therapy
Red and near-infrared light therapy, also known as photobiomodulation, has garnered increasing attention for its remarkable therapeutic properties. This form of treatment involves exposing tissues to specific wavelengths of red and near-infrared light, which can penetrate deep into the body’s cells. One of the notable benefits of this therapy lies in its potential for aiding in retina repair.
Studies have shown that red and near-infrared light therapy can stimulate cellular activity and enhance mitochondrial function, leading to improved energy production within cells. In the context of the retina, this means that damaged or degenerating cells may experience a boost in their ability to regenerate and repair.
This is particularly promising for conditions affecting the retina, such as age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy.
Furthermore, red and near-infrared light therapy has demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects, which can be crucial in reducing inflammation and swelling associated with retinal disorders. By mitigating inflammation, this therapy supports a healthier environment for cellular repair and regeneration.
In addition to its potential benefits for retina repair, red and near-infrared light therapy has shown promise in various other areas of health, including wound healing, pain relief, and cognitive function. As research continues to uncover the full scope of its therapeutic potential, red and near-infrared light therapy stands as a promising avenue for improving the well-being of individuals affected by retinal conditions and a range of other health concerns.
Click Here To Check Out Mito Red Light In Home Light Therapy Devices
In conclusion, red and near-infrared light therapy represents a compelling frontier in the field of medical treatment. Its ability to harness specific wavelengths of light for cellular rejuvenation holds immense promise, particularly in the realm of retina repair. By stimulating cellular activity, enhancing mitochondrial function, and reducing inflammation, this therapy offers a potential lifeline for individuals grappling with retinal disorders like age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy.
Moreover, the versatility of red and near-infrared light therapy extends beyond retina repair, encompassing a broad spectrum of health benefits. From expediting wound healing to alleviating pain and bolstering cognitive function, its applications are far-reaching and continue to captivate the medical community.
As research advances and our understanding deepens, red and near-infrared light therapy stands as a beacon of hope for those in search of effective, non-invasive treatments. It is poised to revolutionize the way we approach a myriad of health conditions, offering a beacon of light for a brighter, healthier future. With its potential to transform lives, this therapy undoubtedly deserves a prominent place in the arsenal of modern medical interventions.
In Conclusion:
LED and CFL bulbs, while offering energy efficiency and longevity, come with their own set of concerns, particularly in terms of environmental impact and potential health risks due to the presence of substances like mercury and other hazardous materials.
Conversely, the emergence of red and near-infrared light therapy presents a promising paradigm in medical treatment. This innovative approach harnesses specific wavelengths of light to stimulate cellular activity and mitochondrial function, leading to a host of health benefits.
Notably, it shows great potential in retina repair, offering hope to those grappling with retinal conditions such as age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy.
Furthermore, the therapeutic applications of red and near-infrared light extend beyond retina repair. Its ability to reduce inflammation, expedite wound healing, alleviate pain, and enhance cognitive function showcases its versatility and far-reaching potential. As research continues to unravel the depths of its benefits, this therapy holds the promise of revolutionizing the medical landscape.
In navigating the choices in lighting technologies, it is imperative to weigh the advantages and drawbacks of each option. While LED and CFL bulbs offer energy efficiency, their potential environmental and health risks cannot be ignored.
Ultimately, a balanced consideration of these technologies is essential in making informed choices that prioritize both environmental sustainability and personal well-being. With further research and prudent utilization, these advancements in lighting hold the potential to illuminate a healthier, more sustainable future.
Recommended Reading:
Study Finds These Types Of Lights Commonly Found In People’s Homes Can Permanently Damage Your Eyes And Hinder Your Sleep Quality
Water, Acidic, Light – 3 Things You Should Do in The Morning For Gut Health, Energy, Lymphatic Health, Immunity & More