Magnesium is involved in numerous biological processes in the body, playing a crucial role in various physiological functions. Here are just ten of the key biological processes in which magnesium participates:
1. Enzyme Activation: Magnesium is a cofactor for hundreds of enzymes involved in processes like energy metabolism (e.g., ATP synthesis), DNA and RNA synthesis, and protein synthesis.
2. Muscle Contraction and Relaxation: Magnesium is essential for muscle function, including the contraction and relaxation of muscles. It acts as a calcium antagonist, regulating calcium influx into muscle cells.
3. Nervous System Function: Magnesium plays a role in nerve impulse transmission and neuromuscular coordination. It helps regulate neurotransmitter release and neuronal excitability.
4. Energy Production: Magnesium is a critical component of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy carrier in cells. It is involved in ATP synthesis and the function of ATP-dependent enzymes.
5. DNA and RNA Synthesis: Magnesium is required for the activity of enzymes involved in DNA and RNA synthesis, including DNA polymerases and RNA polymerases.
6. Protein Synthesis: Magnesium is involved in the synthesis of proteins, acting as a cofactor for enzymes involved in translation, the process by which mRNA is translated into proteins.
7. Bone Health: Magnesium is essential for bone formation and maintenance. It helps regulate the activity of osteoblasts (cells responsible for bone formation) and is involved in the metabolism of calcium and vitamin D, which are important for bone health.
8. Regulation of Blood Glucose Levels: Magnesium plays a role in insulin action and glucose metabolism. It helps regulate insulin sensitivity and the transport of glucose into cells.
9. Blood Pressure Regulation: Magnesium helps regulate blood pressure by influencing vascular tone and endothelial function. It also plays a role in electrolyte balance, which is important for blood pressure regulation.
10. Immune Function: Magnesium is involved in immune system function, including the activation and function of immune cells such as T cells and macrophages.
These are just a few examples of the many biological processes in which magnesium is involved. Its role is diverse and essential for overall health and well-being.
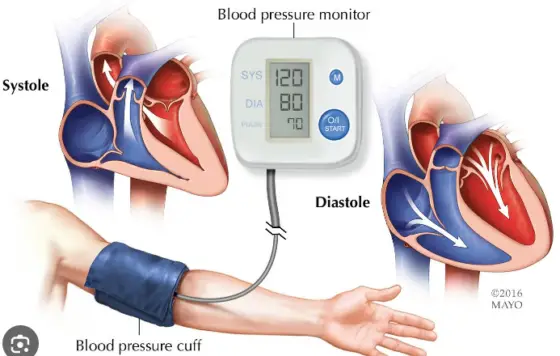
How Does Magnesium Impact Blood Pressure?
Magnesium is so important if you have trouble sleeping or generating energy. This mineral also helps to regulate heart rate and cardiovascular function including but not limited to blood pressure.
Magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure and maintaining overall cardiovascular health. Here’s how it impacts blood pressure:
1. Vasodilation: Magnesium helps blood vessels relax, leading to vasodilation. When blood vessels widen, it reduces resistance to blood flow, which can help lower blood pressure.
2. Calcium Balance: Magnesium works in tandem with calcium to regulate muscle contraction, including the muscles in blood vessel walls. An imbalance between calcium and magnesium levels can lead to increased muscle contraction and vasoconstriction, potentially raising blood pressure.
3. Endothelial Function: Magnesium supports endothelial function, which is vital for maintaining healthy blood vessels. Endothelial cells produce substances that help regulate blood vessel tone and inflammation, influencing blood pressure regulation.
4. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: Magnesium has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress can damage blood vessels, leading to hypertension. Magnesium helps counteract these effects, promoting healthier blood vessel function.
5. Insulin Sensitivity: Magnesium plays a role in insulin sensitivity, and insulin resistance is linked to hypertension and other cardiovascular issues. By improving insulin sensitivity, magnesium may indirectly contribute to better blood pressure regulation.
6. Sympathetic Nervous System: Magnesium helps modulate the activity of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls functions like heart rate and blood pressure. Proper magnesium levels can help prevent excessive sympathetic nervous system activation, which can lead to high blood pressure.
7. Electrolyte Balance: Magnesium works alongside other electrolytes like potassium and sodium to maintain proper fluid balance in cells. Imbalances in these electrolytes can contribute to hypertension, and magnesium helps regulate these balances.
While magnesium has beneficial effects on blood pressure regulation, it’s essential to maintain a balanced diet and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations. In some cases, magnesium supplementation may be recommended for individuals with magnesium deficiency or specific health conditions affecting blood pressure.
Two Magnesium Products That I Take Personally
- Magnesium breakthrough pills: Magnesium breakthrough pills contain six (6) different forms of magnesium for sleep, digestive health, muscles, stress and more! Click here to get magnesium breakthrough. Use the discount code: Healthywildfree at checkout for 10% off!
- Magnesium Chloride Spray: This spray is pure magnesium chloride which is the most universally bioavailable magnesium available. I tend to keep both on hand because the spray works well in specific areas where you may hold tension, tightness or even pain in the body. I get my magnesium spray from Omica Organics. Click here to visit. Use the discount code: Healthywildfree to get 10% off your order.
Recommended Reading: