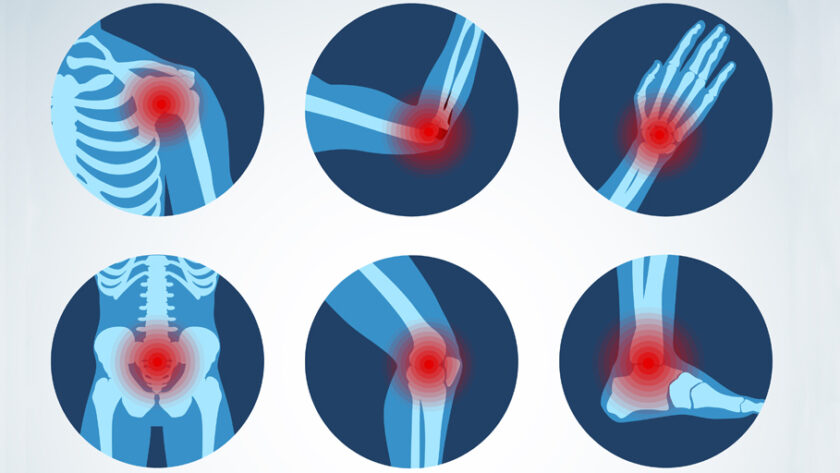
Pain and inflammation go hand in hand. Anywhere in the body. It could be your lower back, your knees, your neck, whatever it may be. When your body is in a state of chronic inflammation pain or tension will be a byproduct of this. What most people don’t realize however is that inflammation is a natural response of the body to protect an area that has been damaged or infected. Think of inflammation like a bubble around a problem area for the body to create space to assess it and act.
Inflammation is a response of the body to protect and correct these areas of the body that need support. The issue arises when inflammation spikes out of control and stays in a state of inflammation. Depending on the severity of the damage, injury or infection the inflammation can last anywhere between a few days to a few weeks. If there is swelling or inflammation that continues your body isn’t moving into the next phase of healing as it’s supposed to.
What is The Difference Between Acute And Chronic Inflammation?
Acute inflammation is a normal immune response to injury or infection. It is characterized by swelling, redness, heat, and pain. It usually occurs rapidly and resolves within a few days or weeks.
Chronic inflammation is a long-term immune response to an ongoing injury or infection. It is characterized by low-grade inflammation that persists for months or years. Chronic inflammation can lead to the development of diseases such as asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancer.
In general, acute inflammation is a normal and necessary process that helps to protect the body from harm and promote healing. Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, can be harmful and may lead to tissue damage and disease.
The question then becomes what creates inflammation in the first place? What leads to inflammation to occur in the body.
What Causes Inflammation To Become Chronic?
There are many causes of inflammation, most of which come from our diet and what we put in our mouth. Foods and drinks. However, stress causes inflammation in the body as well. So pay attention to the stressful environments and circumstances that you put yourself in. Here are some of the top foods and drinks that cause acute inflammation to become chronic:
There is no specific list of foods or drinks that cause inflammation in everyone. We have bioindividuality and what may cause inflammation in my body may not in yours, and vice versa. Some people may be more sensitive to certain foods and experience inflammation as a result, while others may not. However, some foods and drinks are generally considered to be pro-inflammatory and may contribute to inflammation in some people. These include:
- Refined carbohydrates: white bread, pasta, pastries, and other foods made with refined grains can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar, which can trigger inflammation.
- Processed meats: meats that have been preserved by smoking, curing, or salting, such as bacon, ham, and hot dogs, are high in saturated fat and have been linked to inflammation. Meat that has been fed GMO feed such as fast food or regular meat at the grocery store are fed GMO feed and this alone will be inflammatory. Organic, grass fed and finished meat or wild caught is much less inflammatory however.
- Fried foods: deep-fried foods are high in unhealthy fats, which can contribute to inflammation. Avoid foods fried in oils.
- Sugary drinks: soda, fruit juices, and other sugary drinks can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar, which can trigger inflammation. Liquid sugar is the worst form of sugar because it has no buffer of fiber, fat or protein to slow the absorption rate.
- Alcohol: heavy alcohol consumption has been linked to inflammation and a higher risk of several chronic diseases.
If you can reduce or eliminate these things from your diet it will reduce the state of chronic inflammation in your body as a whole. You can also support the body by giving your body anti-inflammatory spices and herbs that help to reduce the state of chronic inflammation so that it can be reduced and pain can be reduced as well.
What is The Best Way To Reduce Inflammation?
There are many ways to reduce inflammation in the body and facilitate the body in it’s natural healing response. Inflammation and swelling go hand in hand. Inflammation and pain also go hand in hand. Out
- A study published in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine found that a turmeric supplement was effective in reducing inflammation and improving symptoms in people with osteoarthritis.
- A study published in the Journal of Clinical Rheumatology found that a combination of turmeric and ginger was effective in reducing inflammation and improving function in people with knee osteoarthritis.
- A study published in the journal Arthritis found that a turmeric extract was effective in reducing inflammation and improving symptoms in people with rheumatoid arthritis.
- A review of several studies published in the Journal of Medicinal Food concluded that turmeric may be effective in reducing inflammation and improving symptoms in people with inflammatory conditions, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
It is important to note that these studies were conducted using turmeric supplements, not the spice itself. It is not clear how much turmeric would need to be consumed through diet to achieve similar effects. It is also important to note that turmeric is just one of many strategies that can be used to reduce inflammation. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and other lifestyle factors can also be effective in reducing inflammation.
This is why I recommend Turmeric from Omica Organics. You can get that by clicking here. Use the discount code: VFDF7M for 10% off your order. This organic is biodynamic as well as organic. This means that there are absolutely no chemicals used, which is better than organic! They also have a turmeric ginger blend which will not only reduce inflammation but increase circulation as well.
Fermented (Cultured) Foods & Drinks Reduce Inflammation
Fermented foods are foods that have been through a process of fermentation, a process in which bacteria or yeast convert sugars into alcohol or acids. Some examples of fermented foods include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and pickles.
There is some evidence to suggest that fermented foods may have anti-inflammatory effects. Fermented foods contain probiotics, which are live microorganisms that are similar to the beneficial bacteria that live in the human gut. Some studies have shown that probiotics may help to reduce inflammation in the body.
For example, a review of several studies found that probiotics may help to reduce inflammation in the gut and improve symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Another study found that probiotics may reduce inflammation and improve symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
Visit FermentationMethod.com to learn how to create your own fermented foods and drinks and turn your kitchen into a probiotic factory.
There Are Multiple Inflammation Pathways:
There are several pathways involved in the inflammatory response in the body. These pathways involve a complex interplay of various signaling molecules, immune cells, and other factors that help to regulate inflammation. Some of the key pathways involved in inflammation include:
- The classical pathway: This pathway is initiated by the activation of immune cells called mast cells and basophils, which release chemical mediators such as histamine and leukotrienes. These mediators cause blood vessels to dilate and become more permeable, leading to increased blood flow and the accumulation of immune cells in the affected area.
- The alternative pathway: This pathway is activated by the activation of complement proteins, which are part of the immune system. Complement proteins help to identify and eliminate foreign invaders such as bacteria and viruses, and also play a role in inflammation.
- The toll-like receptor (TLR) pathway: This pathway is activated by the recognition of specific molecules called ligands by TLRs, which are found on the surface of immune cells. TLRs recognize ligands such as bacterial lipopolysaccharides and viral RNA, and trigger an inflammatory response in order to eliminate the invading pathogen.
- The cytokine pathway: This pathway is initiated by the release of cytokines, which are signaling molecules produced by immune cells. Cytokines help to coordinate the immune response and promote inflammation.
There may be other pathways involved in the inflammatory response as well, and the specific pathways that are activated can vary depending on the type and location of the inflammatory response.
What’s important to know is that turmeric helps to down regulate more inflammation pathways than anything else in nature. it has the most research showing how anti-inflammatory it is.
This is why I personally use and recommend Omica Organics turmeric. This turmeric is organic as well as biodynamic. It has a brighter color, a stronger smell and is far healthier than regular organic turmeric from the store. I’ve compared them side by side. You can see, taste and smell the difference in quality. Visit Omica Organics by clicking here. Use the discount code: VFDF7M for 10% off.