There’s a vitamin that the majority of the population is deficient in and it plays a role in cellular energy, which manifests itself in your physical energy levels. If you feel that you have low energy, there’s a good chance you’re in this 81 percentile.
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in maintaining good health. It is also known as the “energy vitamin” because of its ability to boost energy levels and fight fatigue. In this article, we will explore the health benefits of vitamin B12, the cofactors needed for its absorption, the top 10 foods with vitamin B12, and more.
Health Benefits of Vitamin B12:
- Supports Healthy Nerve Function: Vitamin B12 is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system. It helps maintain the myelin sheath that surrounds and protects nerves, ensuring that messages are transmitted properly between the brain and the rest of the body.
- Maintains Red Blood Cells: Vitamin B12 is crucial for the production of red blood cells. Without enough B12, the body cannot produce enough healthy red blood cells, which can lead to anemia.
- Promotes Brain Health: Vitamin B12 is important for cognitive health and may help reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline. It is also involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters that regulate mood, such as serotonin and dopamine.
- Boosts Energy Levels: As mentioned earlier, vitamin B12 is known as the “energy vitamin.” It helps convert food into energy and can help combat fatigue. In fact, b12 is often called ‘the energy vitamin’
How B12 Influences Your DNA:
Vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in many cellular processes, including the maintenance of DNA. DNA is the genetic material that carries instructions for the development, growth, and function of all living organisms. The proper functioning of DNA is essential for the healthy growth and repair of cells and tissues.
One of the ways that vitamin B12 influences DNA is by participating in the synthesis of nucleotides, which are the building blocks of DNA. Nucleotides are made up of a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and a phosphate group. Vitamin B12 is involved in the conversion of homocysteine, an amino acid, into methionine, another amino acid that is essential for the synthesis of nucleotides.
Methionine is also important for the methylation of DNA. Methylation is a process that involves the addition of a methyl group to DNA, which can turn genes on or off. This is where epigenetic factors come into play. Genes (such as disease oriented ones) can be turned on or off. Genes are active or inactive based on the environment that they are in. This process is important for regulating gene expression, which is essential for the proper development and function of cells and tissues.
Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to an increase in homocysteine levels and a decrease in methionine levels, which can result in impaired DNA synthesis and methylation. This can lead to DNA damage, which can contribute to a variety of health problems, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.
In addition to its role in DNA synthesis and methylation, vitamin B12 also plays a role in the repair of DNA damage. DNA damage can occur as a result of exposure to environmental toxins, radiation, and oxidative stress. Vitamin B12 is involved in the repair of DNA damage by activating enzymes that repair DNA.
In conclusion, vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in the maintenance of DNA by participating in the synthesis of nucleotides, the methylation of DNA, and the repair of DNA damage. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can impair these processes, leading to DNA damage and an increased risk of health problems. It is important to ensure adequate intake of vitamin B12 through a balanced diet or supplementation to maintain healthy DNA and overall health.
Cofactors Needed for Vitamin B12 Absorption:
Vitamin B12 requires several cofactors for proper absorption. One of the most important cofactors is intrinsic factor, a protein produced in the stomach that binds to B12 and allows it to be absorbed in the small intestine. Other cofactors include calcium, folate, and vitamin B6.
How Vitamin B12 Breaks Down in The Body
Before calcium, foliate and vitamin b6 are important. But there are more nutrients needed to break this down.
Vitamin B12 is a complex nutrient that requires specific enzymes and conditions for its proper absorption and utilization by the body. The digestion and absorption of vitamin B12 involve several steps, including the secretion of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in the stomach and the action of enzymes in the small intestine.
The first step in the digestion of vitamin B12 is the release of HCl in the stomach. HCl serves several functions in the digestive process, including activating pepsin, an enzyme that breaks down proteins, and creating an acidic environment that facilitates the breakdown and absorption of nutrients.
Once vitamin B12 is released from food, it binds with intrinsic factor (IF), a protein produced by the stomach lining. The IF-B12 complex then travels to the small intestine, where it is further broken down by enzymes.
In the small intestine, pancreatic enzymes, such as trypsin and chymotrypsin, continue the breakdown of the IF-B12 complex, allowing B12 to be released and absorbed by the body. The final step in B12 absorption occurs in the ileum, the last part of the small intestine, where B12 is transported across the intestinal wall and into the bloodstream.
The proper digestion and absorption of vitamin B12 are essential for maintaining healthy nerve function, red blood cell production, and brain health. In some cases, individuals may have a deficiency in the enzymes needed to break down and absorb vitamin B12, leading to a deficiency in this important nutrient.
Certain factors can also interfere with the absorption of vitamin B12, such as medications that reduce stomach acid production, gastrointestinal surgery, and certain medical conditions, such as pernicious anemia.
In conclusion, the digestion and absorption of vitamin B12 are complex processes that require the release of hydrochloric acid in the stomach and the action of specific enzymes in the small intestine. Proper digestion and absorption of B12 are crucial for maintaining good health and preventing deficiency. If you suspect you may have a deficiency in vitamin B12, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider, who can evaluate your symptoms and perform diagnostic tests to determine if supplementation is necessary.
Recommended Products For Absorption:
HCL capsules from Bioptimizers – Click to visit.
Digestive Enzymes from Bioptimizers – Click to visit.
Use the discount code: healthywildfree for a discount at checkout for the two products above.
Apple Cider Vinegar Pills – Click here to get 15% off your order.
Apple cider vinegar helps the body to produce HCL which helps the body to absorb vitamin b12.
Organ Meat – Beef Liver, Heart & Kidney Capsules – Click Here To Get 15% Off!
These capsules contain high amounts of vitamin b12, as well as b6 which is a cofactor nutrient.
Click here to visit the paleovalley store (15% off) and get both ACV capsules and organ meat (b6 & b12 sources) all organic.
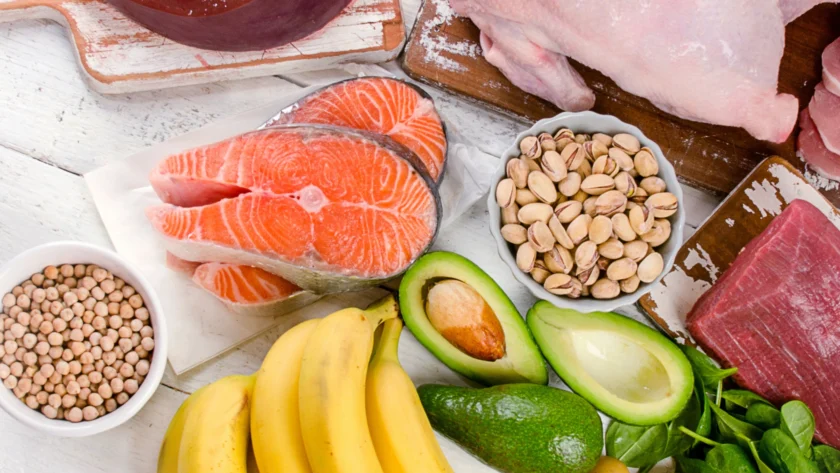
Top 8 Foods with Vitamin B12:
- Clams: 84 mcg per 3-ounce serving
- Beef liver: 70.7 mcg per 3-ounce serving
>> These capsules contains beef liver, kidney liver and heart liver which are rich in b12, b6 (a cofactor nutrient) and many other minerals that support the absorption of b12. Click here to get 15% off your first order!)
- Trout: 5.4 mcg per 3-ounce serving
- Salmon: 4.9 mcg per 3-ounce serving
- Tuna: 2.5 mcg per 3-ounce serving
- Beef: 1.5-2.8 mcg per 3-ounce serving
- Yogurt: 1.4 mcg per 6-ounce serving
- Cheese: 0.2-2.4 mcg per 1-ounce serving
It is important to note that vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal-based foods, so vegetarians and vegans may need to supplement with B12 or consume fortified foods to ensure they are getting enough.
In conclusion, vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient with numerous health benefits. It is important for nerve function, red blood cell production, brain health, and energy levels. To ensure proper absorption of B12, it is important to consume adequate amounts of the cofactors mentioned earlier. Additionally, incorporating foods rich in vitamin B12 into your diet can help ensure that you are getting enough of this important nutrient.
Watch Out For The Synthetic B12 Vitamin:
There’s a synthetic vitamin b12 going around touted as the real thing known as cyanocobalamin, this is a synthetically produced vitamin in a lab and it is NOT the same thing. It is low quality and toxic to the body, it is not worth buying or consuming at all.
Potential Reasons For B12 Deficiency:
Listed reasons for a b12 deficiency could vast but the main potential causes are a vegetarian, vegan or plant based diet as the majority of vitamin b12 sources are from animals and animal products. Additionally R.O processed water used for drinking purpose were found to be independently associated factors for vitamin B12 deficiency. This is because RO (reverse osmosis) water removes minerals from the water. The challenge here is that reverse osmosis water also removes the chemicals and contamination as well. If you add minerals like this essential electrolytes mix from paleovalley into the mix (get 15% off here) I’d venture to say that you’re alright, as long as you are replenishing these essential minerals for hydration and body health.
Best Vitamin B12 Source:
By far the best source of B12 (and b6, a co-factor nutrient) along with many other minerals and vitamins is an Organ supplement. I use the organ complex from paleovalley because it is grass-fed, organic and contains beef liver, beef kidneys and beef heart. These are great sources of COQ10, all the b-vitamins, selenium, phosphorus, zinc, copper and more!