Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide, and its prevalence is increasing at an alarming rate. Roughly one in 10 Americans already have incurable diabetes, which makes it the seventh leading cause of death in the United States. The disease is projected to rise by 700% in younger generations to come.
While genetics and lifestyle factors play a significant role in the development of this disease, a new study has revealed that certain common foods may be contributing to the rise in type 2 diabetes cases.
The study found that seven specific foods are responsible for a staggering 14 million cases of type 2 diabetes globally. The results are shocking, and they underscore the importance of understanding the impact of our food choices on our health. In this article, we will explore the findings of this groundbreaking study and what they mean for individuals and public health efforts.
Understanding The Difference Between Type 1 Diabetes & Type 2 Diabetes
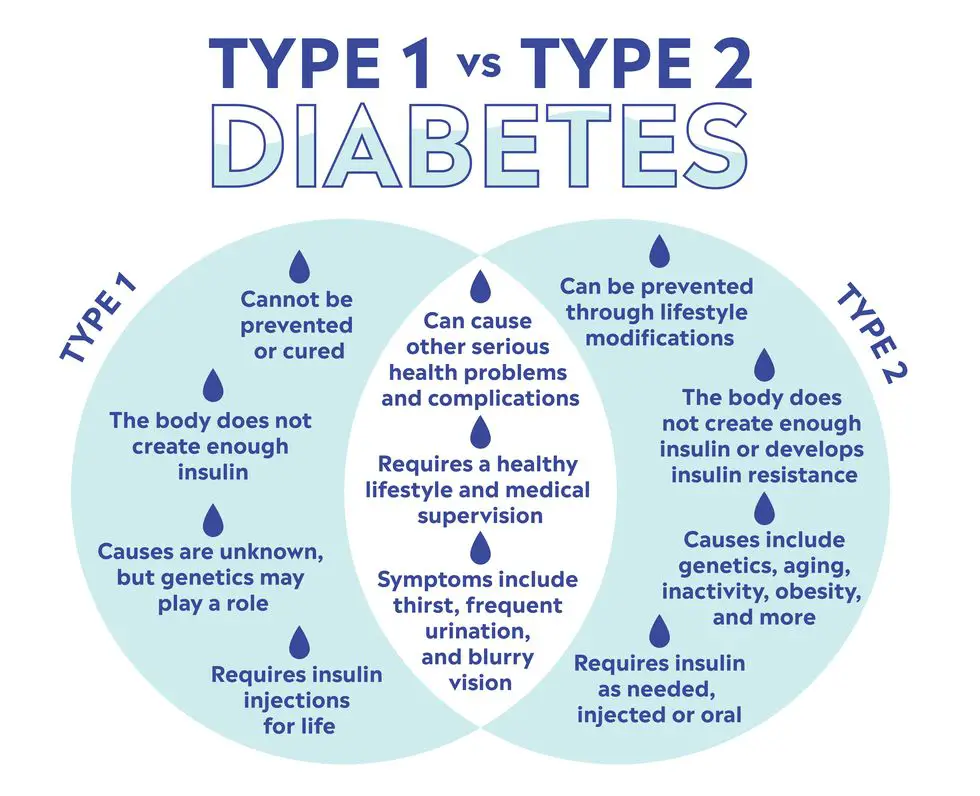
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes are two different forms of diabetes, a condition that affects the body’s ability to produce or use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels and enables the body to use glucose for energy.
Type 1 diabetes, which is also known as juvenile diabetes, usually develops during childhood or adolescence. In this form of diabetes, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin.
As a result, people with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections to regulate their blood sugar levels. The exact cause of this autoimmune response is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Many people believe it to be ensued by chemical pesticides that are sprayed on our foods, and artificial sweeteners that are illegal in many other countries.
Genetic factors may also play a role in the development of type 1 diabetes. People with certain genes are more susceptible to the condition, although having these genes does not necessarily mean that someone will develop type 1 diabetes. Environmental triggers, such as exposure to viruses, may also contribute to the development of the condition in people who are genetically predisposed to it.
Type 1 diabetes can occur at any age, but it is most commonly diagnosed in children and young adults. Symptoms may include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision. If left untreated, type 1 diabetes can lead to serious complications such as nerve damage, kidney damage, and cardiovascular disease.
Managing type 1 diabetes typically involves insulin therapy, either through injections or an insulin pump, as well as regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and dietary management. While there is currently no cure for type 1 diabetes, advances in treatment and management have significantly improved the prognosis and quality of life for people with the condition.
Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, typically develops in adults and is associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet. In this form of diabetes, the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin, and the pancreas may not be able to produce enough insulin to compensate for this resistance.
Type 2 diabetes can often be managed through lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, but some people may also require medication or insulin therapy.
Overall, while both forms of diabetes involve problems with insulin regulation, they have different causes and may require different treatment approaches. It’s essential to understand the differences between the two types of diabetes to manage the condition effectively and minimize the risk of complications.
Could Neem Oil Be The Answer To Treating Diabetes And Other Diseases
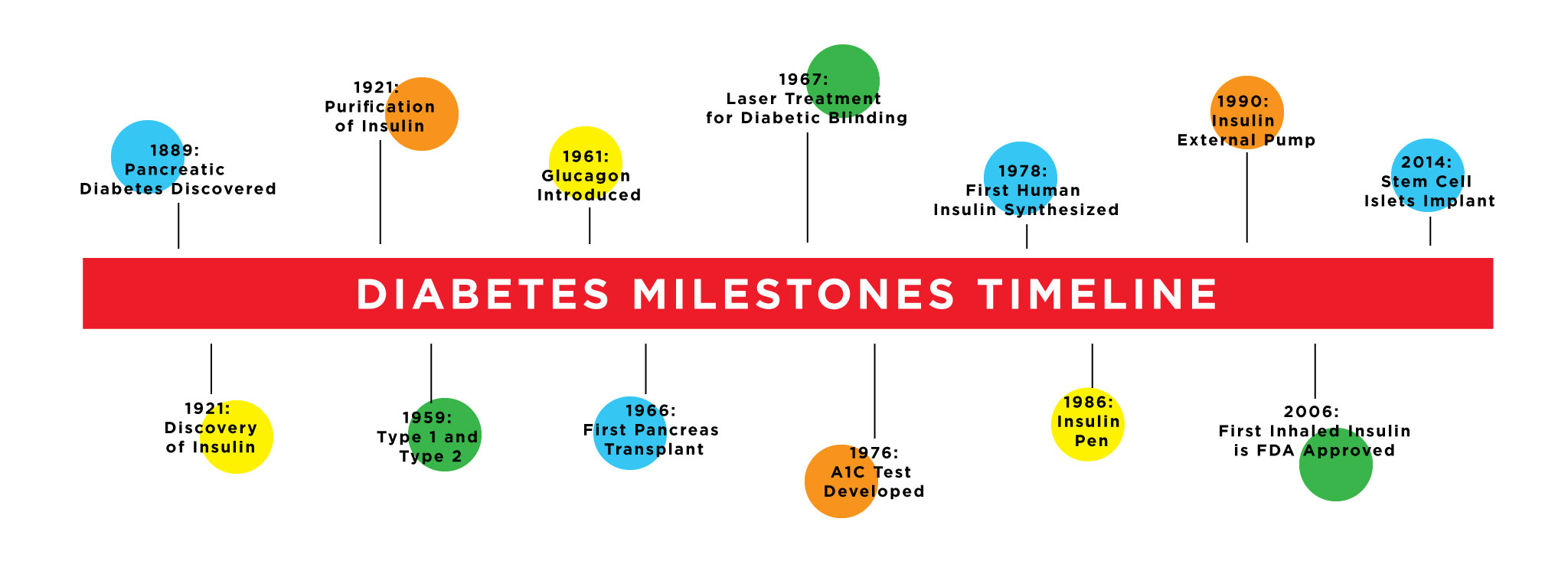
History Of Diabetes
Between 1980 and 2020–2021, the number of adults with diabetes (90% of which is Type 2 Diabetes) increased from 108 million to 537 million, with corresponding increases in obesity from 100 million to 764 million adults. As this is a global phenomenon, no nation has experienced a decline in diabetes or obesity in the last 40 years.
Diabetes creates extraordinary burdens on individuals, families, nations and healthcare systems, causing one in eight global deaths and increasing risk of cardiovascular diseases, renal decline, fatty liver disease, blindness, cancers, coronavirus disease 2019 and other infectious diseases.
The Results
Eleven dietary factors had convincing evidence of contributing to Type 2 Diabetes or weight gain. These included insufficient intake of fruits, non-starchy vegetables, nuts and seeds, whole grains, and fermented foods. The latter included excess intake of potatoes, refined rice and wheat, processed meats, unprocessed red meats, sugar sweetened beverages, and fruit juices.
The unprocessed red meats could be attributed to the unnatural diet that most farm animals are fed, which include GMO corn, soy, and wheat.
In fact, it was unclear in the data presented in the study if Genetically modified foods were considered. With the rise of sickness, versus the rise of genetically modified foods in parallel, it would not surprise me in the least bit if they are connected. It should at least be considered, in my humble opinion.
In 2018, based on Global Burden of Disease data, 20 million new Type 2 Diabetes cases occurred among adults globally, with the greatest absolute number of annual new cases occurring in southeast and East Asia and South Asia.
Findings implicate excess refined rice and wheat (like processed cereals and other processed foods) and insufficient whole grains as a leading driver of diet-attributable type 2 diabetes globally.
The Take-Away
Dealing with Type 2 diabetes can be debilitating, but it doesn’t have to be. A few simple changes to ones diet can change the course of this disease and improve your quality of life. In fact, adding certain foods, and cutting back on others, can prevent, treat, and even reverse many common diseases.
Consider adding more fresh fruits, non-starchy vegetables, whole grains (like the ones pictured above), beans, seeds, nuts and legumes and above all, fermented foods. Fermented foods can have a powerful impact on your health.
By boosting your immune system, healing the gut, and promoting nutrient absorption, I would highly recommend to anyone with any ailments to eat at least 1 serving of fermented food a day.
If you’d like to learn how to start making your own fermented foods at home, and even learn how to Reset Your Gut, I suggest you check out:
The Fermentation Method
The Fermentation Method is the most complete fermentation step-by-step guide available online. You’ll learn how to make sourdough bread, sourdough pizza, tortillas, chips, cookies and cinnamon rolls! Additionally, you’ll receive bonus videos on how to make sauerkraut, kimchi, pickles, sourdough bread, coconut yogurt, salsa and water kefir all from scratch!
The findings of the recent study on the link between 7 common foods and 14 million type 2 diabetes cases worldwide are alarming. This new information highlights the need for individuals to pay close attention to their diets and make healthier food choices to minimize their risk of developing this chronic disease.
It also emphasizes the importance of public health efforts to promote healthy eating habits and raise awareness about the link between diet and type 2 diabetes. By taking steps to reduce the consumption of the foods identified in the study, and making other healthy lifestyle choices, we can work together to prevent and manage type 2 diabetes and improve the overall health and well-being of our communities.